Laparoscopy utilizes fiber optics to illuminate the abdomen. It is twice the length of a pen and this laparoscopy procedure is done in the presence of anesthesia. An equipment is kept in the vagina for the movement of the uterus. Carbon dioxide is injected below the naval to isolate the abdominal organs, thereby facilitating the physician to see the reproductive organs. The gas is removed later. Smaller telescopes are utilized in a recently used technique called microlaparoscopy. Small cuts with decreased soreness of the abdomen are seen. Laparascopic surgery is a technique involving a cut of 0.5 to 1.5 cm in the abdomen and pelvic regions.
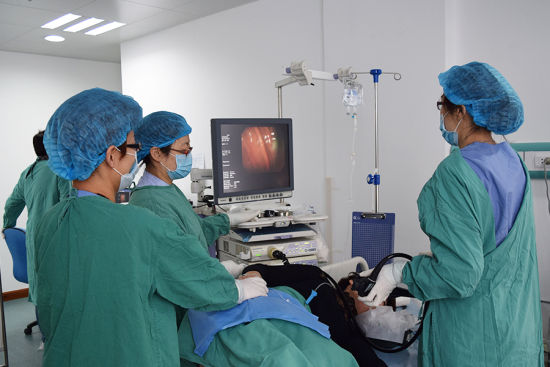
Laparoscopy
Lymph nodes in the pelvis are isolated during a laparoscopic lymphadenectomy for laparoscopy prostate cancer. These nodes are removed through small cuts and processed to the lab for further analysis. Presence of cancer in these nodes reveals the degree of spreading of the cancerous cells.
Endometriosis is common amidst women and the lining tissue of the uterus grows outside the uterus. These are referred to as lesions, tumors, nodules, implants or growths. A finger is placed on the vagina and the other finger is kept on the rectum. It is a painful procedure with lots of discomfort. Pain in the pelvis and other findings aim at endometriosis.
Diagnosis of endometriosis is not inferred by personal assessment or symptoms. Ultrasound helps in eliminating risk of pelvic diseases. A visual check up of the pelvis proves beneficial in diagnosing endometriosis of the vagina and bladder. The most precise way of diagnosis is by incision. This procedure requires less time and is done as an out patient procedure.
The abdomen is initially inflated with carbon dioxide and sterile, surgical equipment called laparoscope is inserted to observe the pelvis and abdomen. Biopsy is also performed, as a part of the procedure in laparoscopy, as they reveal endometrial implants, earlier not visible. Pelvic ultrasound and laparoscopy are also imperative, exclusive of malignancies that show signs that impersonate endometriosis symptoms. The procedure results in shoulder pain and abdominal discomfort. This is attributed to the carbon dioxide remnant in the body. An analgesic is given for relief and recovery is seen after 2 to 3 days. The side effects of the anesthesia are less felt in patients with good health. Abdominal blood vessel damage or pelvic damage are the risks of laparoscopy. Immediate surgery is recommended in such cases. About two in thousand experience these complications.

![Diseases, Symptoms, tcm, [tcmwindow.com]](/uploadFile/adImg/2015/11/11/f5cbfcc0-4df5-4646-9b9a-f316651a0199.jpg)





