The bladder, located in the lower abdomen, is responsible for storing and discharging urine.The water and turbid qi produced in the process of metabolism are changed into urine through qi-transforming function of the kidney and transmitted to the bladder. When certain amount of urine is accumulated in the bladder, it is excreted naturally out of the body through the action of qi-transformation. The storage and excretion of urine by the bladder result from the fixating and qi-transforming functions of qi. Since bladder-qi is controlled by the kidney-qi,the fixating and qi-transforming functions of kidney-qi is key to the storage of urine in the bladder and excretion of urine out of the bladder.
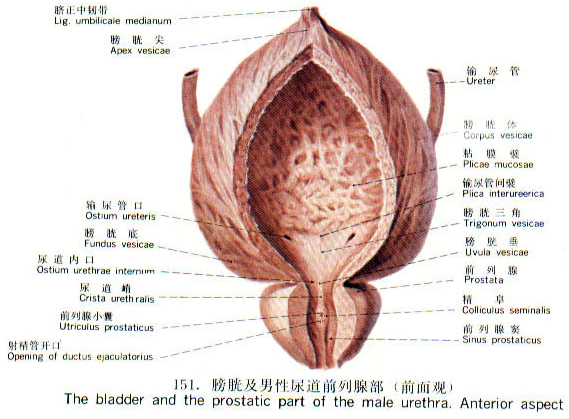
Generally speaking, failure of kidney-qi to fixate and transform qi due to deficiency affects the function of the bladder to excrete urine. If the bladder is attacked by exogenous pathogenic factors, @transformation activity will be affected, also leading to disorder in excreting urine. But the syndrome in the former case is deficiency and the syndrome in the latter case is excess. Deficiency of bladder-qi usually leads to symptoms of polyuria, enuresis and incontinence of urine. Obstructed transformation of qi often brings on symptoms of unsmooth urination, dripping urination and anuria.







