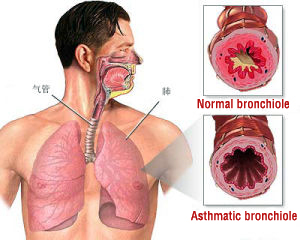
 Asthma, also called bronchial asthma, is defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways, involving various cells particularly mastocyte, eosinophilic granulocyte and T-lymphocyte. It is manifested as paroxysmal wheeze, chest distress and/or cough, which usually occur at night and/or at early morning and may remit spontaneously or by treatment. According to pathogenesis, it may be classified as exogenous asthma and endogenous asthma. The incidence of bronchial asthma is very high, which is a great threat to public health. There are about 100 million patients of asthma in the world, and in China it affects 1% of the population.
Asthma, also called bronchial asthma, is defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways, involving various cells particularly mastocyte, eosinophilic granulocyte and T-lymphocyte. It is manifested as paroxysmal wheeze, chest distress and/or cough, which usually occur at night and/or at early morning and may remit spontaneously or by treatment. According to pathogenesis, it may be classified as exogenous asthma and endogenous asthma. The incidence of bronchial asthma is very high, which is a great threat to public health. There are about 100 million patients of asthma in the world, and in China it affects 1% of the population.
This disease belongs to the category of "xiao zheng"(wheezing syndrome) in TCM. Its pathogenic factors include endopathic and exopathic aspects. The former refers to congenital defect, kidney qi deficiency and weak constitution, or allergic constitution, or the lung obstructed by long-retained phlegm. The latter is related to invasion by exogenous pathogenic factors, improper diet, emotional disturbance, over strain, etc. Phlegm, as the principal pathogenic factor, accumulates in the lung and becomes an "obstinate root" of this disease. Because of this, an acute attack of disease may be induced by sudden change of climate, aspiration of allergen, improper diet, and emotional disorder or over strain. Repeated attacks of asthma for long periods can weaken the lung, spleen and kidney. Continue to learn Chinese medicine treatment for Asthma.
Lung qi deficiency may results in failure of weiqi to protect the body against diseases and the disease is more likely to recur due to exogenous pathogenic factors. Spleen deficiency may bring about failure in transporting function and produce phlegm in the lung. Kidney deficiency may cause failure of receiving qi by the kidney; and kidney yang deficiency causes accumulation of pathogenic fluid that may transform into phlegm, while kidney yin deficiency induces hyperactive fire to scorch the body fluid into phlegm, which moves upwards and stays in the lung, thus worsening the condition.