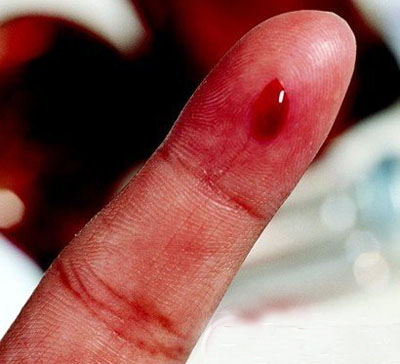
 Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder that slows the blood clotting process. People with this condition experience prolonged bleeding or oozing following an injury, surgery, or having a tooth pulled. In severe cases of hemophilia, continuous bleeding occurs after minor trauma or even in the absence of injury (spontaneous bleeding). Serious complications can result from bleeding into the joints, muscles, brain, or other internal organs. Milder forms of hemophilia do not necessarily involve spontaneous bleeding, and the condition may not become apparent until abnormal bleeding occurs following surgery or a serious injury.
The major types of this condition are hemophilia A (also known as classic hemophilia or factor VIII deficiency) and hemophilia B (also known as Christmas disease or factor IX deficiency). Although the two types have very similar signs and symptoms, they are caused by mutations in different genes. People with an unusual form of hemophilia B, known as hemophilia B Leyden, experience episodes of excessive bleeding in childhood but have few bleeding problems after puberty.