Introduction to Bronchial
Asthma
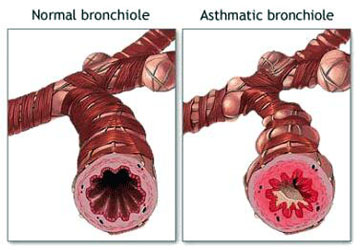
Bronchial asthma refers to the response of the tracheobroncial tree to several stimuli. This causes paroxysmal constriction of the bronchial asthma. The word bronchial asthma is used to differential the condition from cardiac asthma which is caused due to heart failure. Both the conditions have a few similar symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath, but occur due to different causes.
Bronchial asthma is a lung disease whereby the there is obstructive disturbance of the ventilation of the respiratory passage way. There is resistance to the flow of the air in the air passages. The respiratory musculature is not able to provide sufficient gas exchange. This results in a asthma attack with bronchial musculature, edematous swelling of bronchial wall and an increase in the mucous secretion.
In the beginning, the patient can be be free of symptoms during the intervals of the attack. But as it gradually progresses, more mucus is secreted in between the asthma attacks, which builds in our airways and causes bacterial infections, which are secondary in nature.