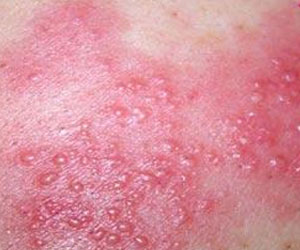
Herpes zoster refers to an acute herpetic dermal disease caused by varicella-zoster virus, clinically characterized by a cluster of blisters distributed like a belt along one side of the body, similar to a snake shape, and serious pain. Clinically, those with primary infection (without immunity) are manifested by chickenpox or insidious infection. When virus enters the cutaneous sensory neural endings, it moves toward the center along neural fibers and is persistently latent in the neurons of ganglions on the posterior spinal neural roots. When the immune function of the host cell subsides, for instance in menstruation, some infectious diseases (common cold), malignant tumors, traumatic injury, radiotherapy, some medications (such as arsenic, stibium, immune inhibitor) and overstrain, etc.