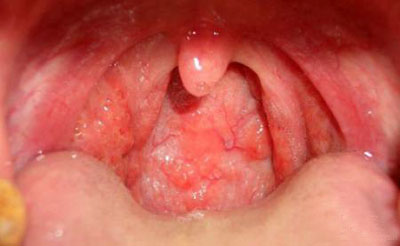
Acute laryngitis is the acute inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa. It is one of the commonly-seen acute infectious diseases of respiratory tract. It is often the secondary disease of acute rhinitis and acute pharyngitis. The disease mostly occurs in the two seasons of winter and spring, with a higher sick rate in males. The disease is more serious if it occurs in children. When the body resistance declines, the disease is mostly the secondary disease of bacterial infection with the previous viral invasion.
The inducing pathogenic factors of the disease include the stimulation of dust and harmful gases, improper use or overuse of voice, trauma, heavy smoking and excessive drinking. When diffuse congestion forms in the laryngeal mucosa, infiltration will arise in the round cells and polymorphonuclear cells, causing tissue edema, even epithelial injury and exuviation to form superficial ulcer. This is the pathological process of the disease.