Introduction to
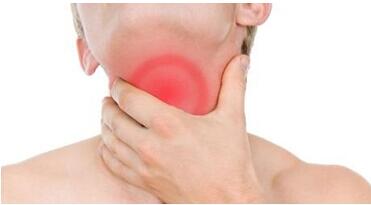
Hashimoto’s ThyroiditisHashimoto’s thyroiditis very often results in hypothyroidism with bouts of hyperthyroidism. Symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis include weight gain, depression, mania, sensitivity to heat and cold, paresthesia, chronic fatigue, panic attacks, bradycardia, tachycardia, congestive heart failure, high cholesterol, reactive hypoglycemia, constipation, migraines, muscle weakness, joint stiffness, menorrhagia, myxedematous psychosis, cramps, memory loss, vision problems, infertility and hair loss.
The thyroid gland may become firm, large, and lobulated in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, but changes in the thyroid can also be nonpalpable. Enlargement of the thyroid is due to lymphocytic infiltration and fibrosis rather than tissue hypertrophy. Physiologically, antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and/or thyroglobulin cause gradual destruction of follicles in the thyroid gland. Accordingly, the disease can be detected clinically by looking for these antibodies in the blood. It is also characterized by invasion of the thyroid tissue by leukocytes, mainly T-lymphocytes. It is associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma.