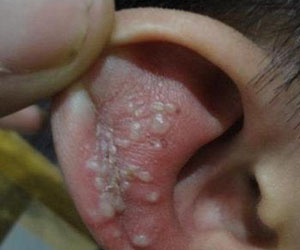
Eczema of external ear refers to the eczema occurring on the external auditory canal, auricle and the skin around these areas. Clinically, the disease manifests as polymorphic injuries of the local skin of the external ear such as flush, blister, exudate, erosion and crust. It can be divided into three types: acute, subacute and chronic ones. Infants are susceptible to the disease, especially infants of allergic constitution and often with the complication of facial eczema.
The pathogenic factors and pathogenesis of eczema have not been understood so far. Possibly, the disease is related to the allergic reaction, mental factors, dysneuria, endocrine disorder, metabolic dysfunction, indigestion, etc. It is generally believed that allergic reaction plays a dominant role. Clinically, infants with eczema are indeed of allergic constitution in most cases.